 evolution, theory in biology postulating that the various types of plants, animals, and other living things on Earth have their origin in other preexisting types and that the distinguishable differences are due to modifications in successive generations.
evolution, theory in biology postulating that the various types of plants, animals, and other living things on Earth have their origin in other preexisting types and that the distinguishable differences are due to modifications in successive generations.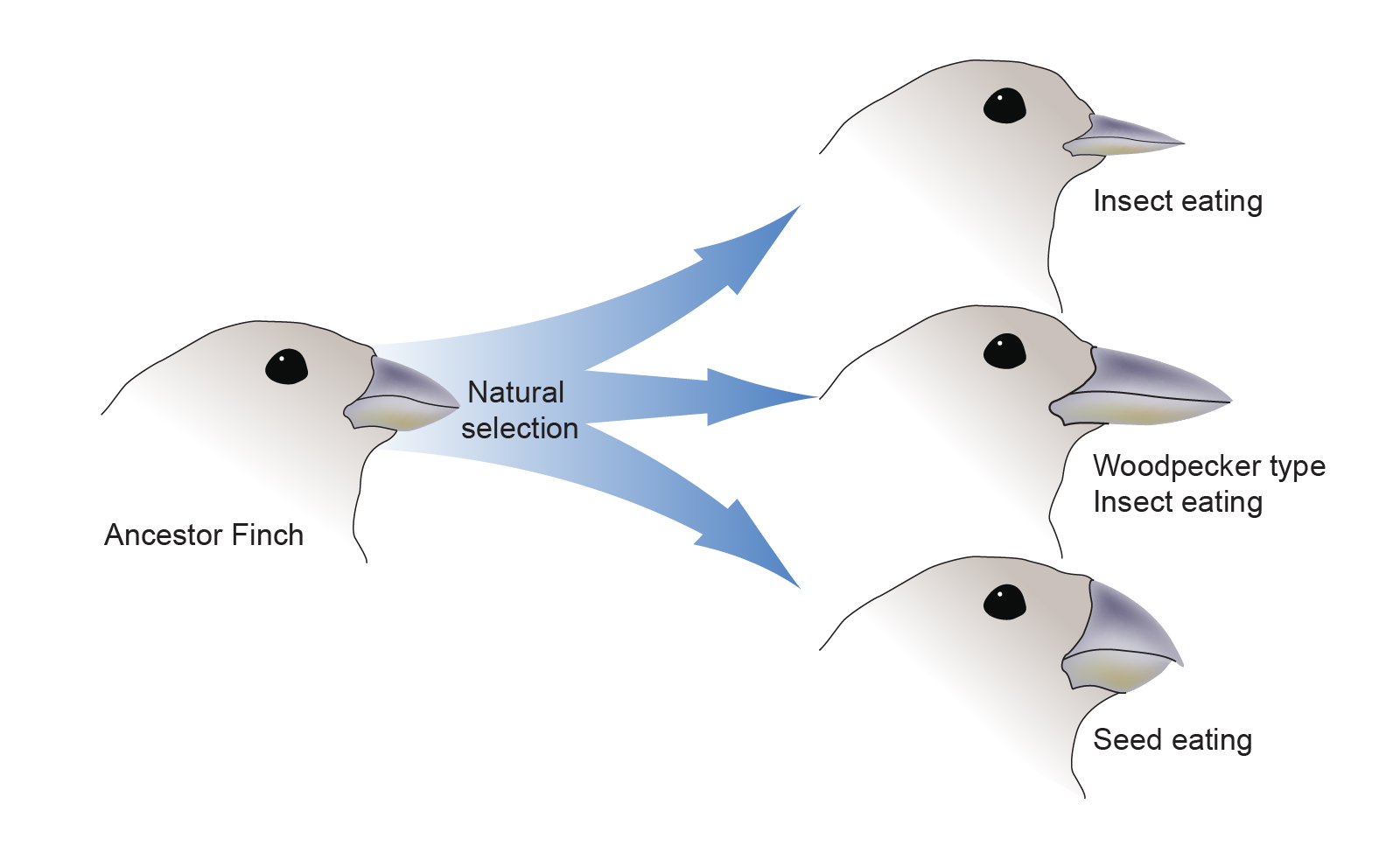 Evolution, as related to genomics, refers to the process by which living organisms change over time through changes in the genome. Such evolutionary changes result from mutations that produce genomic variation, giving rise to individuals whose biological functions or physical traits are altered.
Evolution, as related to genomics, refers to the process by which living organisms change over time through changes in the genome. Such evolutionary changes result from mutations that produce genomic variation, giving rise to individuals whose biological functions or physical traits are altered. Biological evolution is the process of change and diversification of living things over time, and it affects all aspects of their lives— morphology (form and structure), physiology, behaviour, and ecology.
Biological evolution is the process of change and diversification of living things over time, and it affects all aspects of their lives— morphology (form and structure), physiology, behaviour, and ecology.